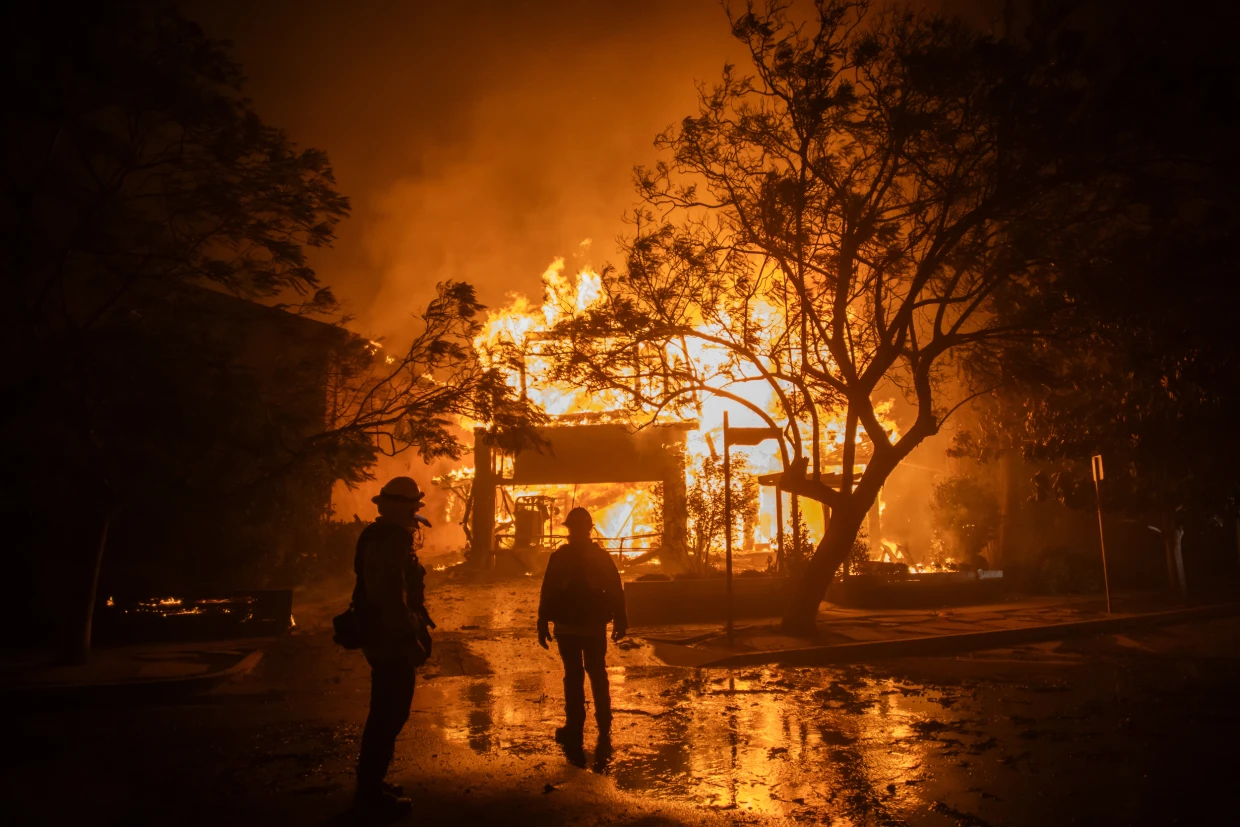
As wildfires continue to rage across various regions, one of the most devastating aspects of these natural disasters is the destruction of homes and communities. The phrase “the homes serve as fuel for the fire” poignantly captures the tragic reality that many residences and structures are not only vulnerable to wildfires but can also inadvertently contribute to their spread.
1. How Homes Contribute to the Spread of Wildfires
In many wildfire-prone areas, homes are often located in or near forests, grasslands, and other natural landscapes that are susceptible to fires. These homes, particularly those made of wood or other flammable materials, act as fuel that can exacerbate the fire’s intensity and spread.
- Flammable Building Materials: Many homes in wildfire-prone regions are constructed with materials that are highly flammable, such as wood siding, roofing, and decks. In the event of a wildfire, these materials can catch fire quickly, allowing the blaze to grow exponentially.
- Landscaping Choices: Poor landscaping choices, such as the use of dry shrubs, trees with low moisture content, or wood piles near homes, can provide an additional fuel source for wildfires. This is often a result of insufficient building codes or a lack of awareness regarding fire safety.
- Fire-Resistant Zones: In areas where wildfires are common, it’s crucial for homes to be surrounded by defensible space – a fire-resistant zone that can help slow the spread of the fire. Without proper clearance of vegetation and fire-resistant materials, homes become increasingly vulnerable to fires.
2. The Destructive Power of Wildfires
Once a wildfire ignites, the destruction it causes is not just limited to the homes it consumes. Wildfires can have a far-reaching impact on the environment, economy, and public health.
- Environmental Damage: Wildfires often lead to the destruction of habitats, loss of biodiversity, and severe soil erosion. When homes in these areas are destroyed, they contribute to the overall environmental degradation caused by the fire.
- Economic Impact: The loss of homes and businesses can have a significant economic impact, particularly in areas where tourism or local industries rely on the natural environment. Rebuilding costs for communities can be astronomical, often leading to long-term financial strain for residents and local governments.
- Health and Safety Risks: The smoke from wildfires poses serious health risks, particularly to people with respiratory conditions. When homes are destroyed, the air quality in surrounding areas can worsen, exacerbating health issues and forcing residents to evacuate or seek emergency medical care.
3. Preventive Measures and Solutions
While it’s difficult to prevent wildfires entirely, there are several strategies that can be employed to reduce the risk of homes serving as fuel for the fire. These measures can help protect communities and potentially save lives.
- Fire-Resistant Materials: Building homes with fire-resistant materials such as concrete, metal, and non-combustible roofing can significantly reduce the chances of homes catching fire. In addition, installing fire-resistant windows and doors can help minimize damage.
- Creating Defensible Space: Homeowners can create a defensible space around their property by clearing away dead vegetation, trimming trees, and removing any debris that could serve as fuel for the fire. Fire-resistant landscaping, such as using low-moisture plants, can also make a big difference.
- Fire-Resistant Communities: Local governments can enact and enforce building codes that require new homes in wildfire-prone areas to be constructed with fire-resistant materials and landscaping. In addition, establishing firebreaks—gaps in vegetation that can prevent a fire from spreading—can be an effective strategy to protect communities.
- Early Detection and Preparedness: Improved early warning systems and fire detection technology can help reduce the impact of wildfires. Encouraging homeowners to install fire alarms and sprinkler systems can also help protect homes.
4. The Role of Technology and Innovation
Advancements in technology have played a significant role in improving wildfire prevention, detection, and response. These innovations can help save lives and prevent homes from serving as fuel for future fires.
- Drones and AI: Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras are being used to monitor wildfire areas, providing real-time data to firefighters and allowing them to identify hot spots early. Artificial intelligence (AI) is also being used to predict wildfire behavior and identify high-risk areas.
- Fire-Resistant Materials: Innovations in fire-resistant materials and coatings are helping to create safer homes. These new materials are designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames.
- Smart Home Technology: Smart home technology, such as fire alarm systems and sprinklers, can offer advanced protection for homes. These systems can detect smoke and heat, alerting homeowners and emergency responders before the fire spreads too far.
5. Conclusion
The phrase “the homes serve as fuel for the fire” underscores the vulnerability of structures in wildfire-prone areas, where homes can unintentionally contribute to the spread of flames. However, through preventative measures, technological innovations, and stronger building codes, communities can better protect their residents and minimize the devastating impact of wildfires. While the future may hold greater challenges as wildfires become more frequent and intense, the resilience and preparedness of communities will be crucial in ensuring that homes do not simply become fuel for the fire.
Sources: